damping
英 [ˈdæm.pən]
美 [ˈdæm.pən]
- n. [物] 阻尼;[物] 衰减,[物] 减幅
- v. 抑制(damp的ing形式);使潮湿
使用频率:
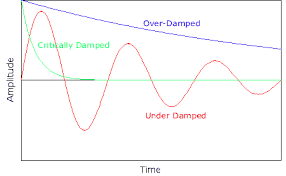
记忆方法
记忆“damping”的方法可以是:将其分解为“dam”和“ping”。想象“dam”(水坝)阻止了某种流动(例如,水流、能量等),而“ping”像一个轻触,暗示这个过程是渐进的、缓和的。这样,“damping”就可以被记忆为减缓或减弱某种流动或振动的动作或状态。
以上内容由AI生成, 仅供参考和借鉴
权威例句
- 1. Theoretically the absence of damping results in an infinite response at resonance.
- 在理论上,无阻尼时将引起无尽的谐振响应.
- 2. Strong damping effects are possible because of solid particles in the chamber.
- 燃烧室内的固体颗粒可能引起强烈的阻尼效应.
- 3. Damping wakes possible finite steady - state vibration amplitude at resonance.
- 在共振时,阻尼可能限制稳定振动的振幅.
- 4. The singularity arises only formally, because we neglected the effect of damping.
- 这个奇异点的产生仅仅是形式上的, 因为我们忽略了阻尼的作用.
- 5. In the laser this damping mechanism can be visualized as follows.
- 在激光器中,这种阻尼机理可以如下理解.